
Duplicate entries in large spreadsheets can skew data analysis and complicate decision-making. Managing customer lists, sales records, or inventory data often requires quick, efficient methods to eliminate such errors. Practical techniques, including how to use Apps Script in Google Sheets for automation, can streamline the cleanup process in under a minute.
Automated approaches reduce the time spent on manual corrections and enhance data reliability. Numerous's Spreadsheet AI Tool provides AI-powered assistance that swiftly identifies and removes duplicates, allowing users to focus on analysis and strategic decision-making.
Summary
Duplicate entries slip into spreadsheets during routine operations like importing CRM data, merging survey responses, or combining reports from different team members, making them difficult to detect until totals stop reconciling or customer counts appear inflated. The degradation happens gradually without warning signals, creating confusion about when the data quality actually declined.
Google Sheets' standard Remove duplicates tool only catches exact matches, meaning "John Smith" with a trailing space and "John Smith" without one both survive the cleanup process. This limitation creates a credibility gap: sheets appear visually clean but still produce unreliable totals because variations in capitalization, spacing, or formatting prevent the tool from recognizing entries as duplicates.
Standardizing data before removing duplicates catches the variations that visual inspection misses. Using helper columns with formulas like LOWER and TRIM to normalize text transforms fuzzy duplicates into exact matches, potentially consolidating a 3,000-row dataset down to 2,400 entries instead of just 2,700, directly improving reporting accuracy and decision confidence.
Multi-column duplicate detection prevents both over-deletion and under-deletion by correctly defining uniqueness. A customer appearing twice with different order dates represents legitimate separate transactions, not duplicates, but manual scanning cannot reliably hold these multi-column patterns in working memory across hundreds of rows.
Pattern-based analysis identifies semantic duplicates that exact matching misses, recognizing that "Microsoft Corporation", "Microsoft Corp.", and "MSFT" likely represent the same entity based on usage patterns rather than character-by-character comparison. This approach becomes essential when merging data from multiple sources where the same company, product, or location appears under multiple acceptable variations.
Recurring cleanup scenarios, such as monthly CRM imports or quarterly vendor reconciliations, benefit most from systems that recognize patterns rather than requiring manual formula setup each cycle.
'Spreadsheet AI Tool' lets teams describe deduplication rules in plain language rather than constructing nested formulas, making cleanup logic portable across data structure changes and eliminating the technical translation step between understanding what needs fixing and actually fixing it.
Table of Contents
Why Removing Duplicates in Google Sheets Is More Frustrating Than It Should Be
Why Most People Remove Duplicates the Slow Way (and Don’t Realize They’re Doing It Wrong)
5 Practical Ways to Remove Duplicates in Google Sheets in Less Than 1 Minute
Why Removing Duplicates in Google Sheets Is More Frustrating Than It Should Be

Removing duplicates in Google Sheets feels harder than it should be. The problem shows up slowly, not all at once. Users don't notice the mess until it is already mixed into the data. This makes every decision about what to keep or delete feel risky and uncertain. Most duplicate entries don't announce themselves. They sneak in during regular work like importing customer lists from a CRM, merging survey responses collected over weeks, copying vendor data from an email into an existing sheet, or combining quarterly reports from different team members. Each action seems harmless at the time.
By the time something feels off, the duplicates are already scattered throughout, hundreds or thousands of rows. Users didn’t make a mistake; they just did normal spreadsheet tasks. This slow decline of the sheet is confusing, as there are no clear warning signals or error messages showing when things went wrong.
What happens when you think your data is clean?
You open a sheet expecting clean data. The columns are labeled, and the formatting looks professional. At first glance, everything seems normal. However, when you calculate totals, they are surprisingly high. You might run a report and discover that the counts don't match what you recorded last week. A quick visual scan shows nothing wrong, since duplicate rows are often far apart, separated by many legitimate entries.
Some duplicates differ by just one character: a trailing space, a capitalization difference, or an extra comma, making them seem unique even when they are the same entity. This difference creates a confusing experience. The sheet looks trustworthy, but gives untrustworthy results. You start to second-guess not just the data but also your own memory and judgment. It's crucial to ensure data accuracy; our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps you identify and resolve discrepancies efficiently.
How does decision-making around duplicates feel?
Once duplicates are found, the focus shifts from finding them to making decisions. Which row should stay? Should it be the first one added, the newest one, or the one with the most complete information? Think about what could happen if you delete the wrong row; it might break a formula somewhere else in the sheet or take away important context that will be needed later.
This hesitation is not just being overly cautious; it shows pattern recognition. Everyone has deleted something that seemed useless, only to later find out that it had the only copy of important information. This experience makes every cleanup task feel delicate. Instead of confidently removing entries, you might stop, compare, check, and worry. Using the best spreadsheet tools can help streamline this process. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool offers powerful solutions to help you manage your data effectively.
What are the consequences of recurring duplicates?
You spend thirty minutes carefully removing duplicates, checking your work, and confirming that the totals finally match expectations. The sheet feels clean, and you can move forward. The next week, after another data import or when a team member adds rows from their local copy, duplicates appear again. You're back where you started, wondering if you missed entries during your first check or if new ones have just appeared. The cleanup becomes a regular task rather than a one-time fix.
What started as a simple maintenance job turns into an ongoing trust issue. You can't confidently tell stakeholders that "the data is clean" because you know it might not stay that way. Using a spreadsheet AI tool like our tool can help automate duplicate detection and ensure your data remains consistent over time.
Why is duplicate removal more time-consuming than expected?
Removing duplicates might seem like a quick job that takes five minutes, but it can actually take much longer than expected. You look through rows by hand, check values across different columns, and sort and re-sort to group similar entries. You also compare timestamps to determine which record is newer, then carefully delete entries while keeping an eye out for formula errors or broken references.
A task you planned for ten minutes can quickly take an hour. This time mismatch can be really frustrating, not only because the process is slow, but also because it distracts you from more important work. Instead of analyzing trends or making decisions, you end up performing repetitive quality control tasks that a system should handle automatically. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool can help streamline this process, allowing you to focus on higher-level tasks.
What emotional challenges arise from cleaning duplicates?
The deepest frustration does not come from the duplicates themselves; it comes from losing confidence. Even after cleanup, questions still linger: Did I catch them all? Are the remaining rows really unique? Can I trust this data for tomorrow's presentation? This uncertainty creates a chain reaction. If the customer list is unreliable, any analysis based on it is questionable. Also, if the inventory counts have duplicates, the reorder calculations could be wrong. One data-quality issue can cast doubt on every decision made afterward.
How can tools help remove duplicates?
Tools like the Spreadsheet AI Tool help teams quickly find patterns in large datasets. This tool makes it much faster than the manual work usually required to find duplicates. By automating the pattern recognition process, teams move from uncertain manual scanning to systematic validation, enabling them to trust the data without advanced technical skills or complex formulas.
Why is the process of removing duplicates fragile?
Removing duplicates is not hard to understand. The steps are simple: find the matching rows, decide which one to keep, and delete the others. But what makes this process tiring is its fragility. One wrong deletion can cause many problems. If you miss one duplicate, it ruins the whole cleaning effort. Also, if you misunderstand the data source, the same problem could come back tomorrow. This process isn’t about solving a puzzle with a clear answer; it’s about handling a weak spot in a system that should feel more stable than it really is. Even with this fragility, many people continue to use methods that perpetuate the problem, often unaware of a better way forward. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps streamline this process and ensure accurate data management.
Related Reading
Why Most People Remove Duplicates the Slow Way (and Don’t Realize They’re Doing It Wrong)
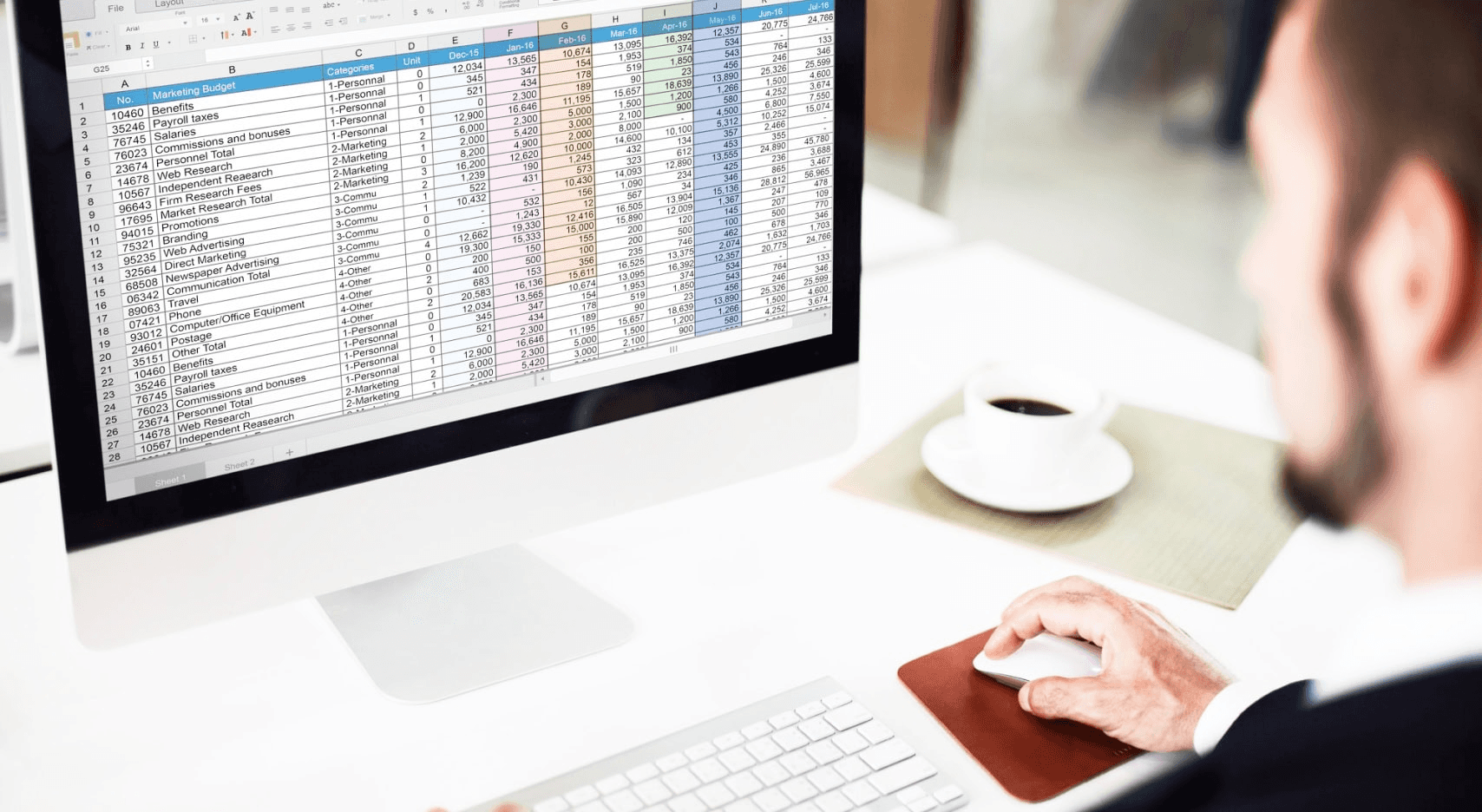

The standard duplicate-removal method taught in millions of YouTube tutorials only catches exact matches. For example, if "John Smith" appears with a trailing space in one row and without it in another, both entries survive the cleanup. This issue also happens with case variations, different formats, and data compiled from multiple sources. Even though it feels like the process is complete because duplicates seem to disappear, what is left is a sheet that still shows the same item listed multiple times in slightly different forms.
When someone types "how to remove duplicates in Google Sheets" into a search engine, they are not looking for detailed data quality strategies; they want a quick solution. YouTube provides just that, often as a two-minute video showing the steps: clicking Data, then Remove duplicates, and finally, Done. This leads to a certain type of learning. The viewer sees the sheet go from messy to clean in seconds. This visual change feels like success. Confidence grows not from understanding the logic behind it, but from seeing an immediate, noticeable result.
What happens when real-world data is involved?
The problem comes up when real-world data is involved. Customer names imported from a CRM retain the formatting from that system. Survey answers collected over months introduce inconsistencies as people type names differently. Vendor lists combined from email attachments have differences that go unnoticed during the merge. None of these details is shown in the tutorial. When the viewer uses the method they learned on their own data, they might notice rows disappearing and think they succeeded. The sheet looks cleaner, and the row counts have decreased, making it appear the job is done. However, differences like "New York" and "new york" or "ABC Corp" and "ABC Corp" stay as separate entries because the tool only removes exact matches.
Why is this approach misleading?
YouTube tutorials often focus on watch time and completion rates. For example, a video that explains data normalization, case sensitivity, and trim functions before showing how to remove duplicates would probably lose viewers within thirty seconds. So, creators go straight to the payoff: the satisfying moment when duplicates disappear. This focus on optimization makes sense for the creator but can mislead the learner. The viewer starts to think that removing duplicates is a single-step process. Click the button, and the problem is solved. No preparation is needed, and no verification is required. This simplicity can seem to be evidence of correctness. When totals still appear wrong after cleanup, users seldom question the method. They often think they missed a step or didn't choose the right range. The idea that the basic approach only deals with some duplicates hardly comes up because the tutorial never mentioned it.
What are the consequences of incomplete duplication removal?
The gap between "removes duplicates" and "removes exact duplicate matches" seems small until you see inflated customer counts that should have been consolidated. A sheet filled with obvious duplicates can cause immediate worry. When you see "Sarah Johnson" repeated ten times in a row, it's clear that something needs to be fixed. After running the standard removal process, the ten identical rows shrink to one, so the visible problem disappears. What is left are the non-obvious duplicates: "Sarah Johnson", "sarah johnson", "Sarah Johnson" (with a space at the end), and "S. Johnson". To assist in identifying and managing these variations effectively, our Spreadsheet AI Tool enhances your data cleaning process.
How does incomplete removal impact data credibility?
Each entry looks different enough that manual scanning often misses them. Formulas that count unique customers see them as four separate individuals. Because of this, reports based on this data show inflated numbers, but they are not so misleading that anyone stops to check them. This creates a credibility gap that is hard to find. When someone asks why the customer count went up by 47, but sales conversations only mention 31 new accounts, there is no clear problem. The data appears clean at first glance, and the process for removing duplicates was correct. However, the numbers do not match. Teams waste hours checking different systems, looking for import errors, and wondering if the CRM is syncing correctly. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps streamline data accuracy and reduce the time spent on such errors.
What is the root cause of the issue?
The actual cause, incomplete deduplication, is often overlooked because everyone thinks that duplicates have already been removed. After all, someone spent thirty minutes using the cleanup tool last week. Forrester Research documented in its 2023 data management report that enterprise datasets grow by 30 to 40 percent each year through routine operations. This growth happens for many reasons, including imports from different systems, recovery copies made during troubleshooting, historical data merged during migrations, and teamwork where members keep local versions that eventually sync back.
How do growth vectors contribute to duplicates?
Each growth vector creates new chances for duplicates to appear with small changes. For instance, an import from the email marketing platform formats company names one way, while the CRM export uses different capitalization. The vendor sheet that is kept by hand has uneven spacing. When all of these are combined into a master sheet, the tool for removing duplicates treats each formatting difference as a unique entry. Small datasets can handle this problem. With 200 rows, you can check for variations by hand after using the automated removal. With 2,000 rows, manual checking gets tiring but is still doable. However, with 20,000 rows, it becomes nearly impossible. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps streamline duplicate removal, making it easier to manage large datasets.
Why does repeating the tool not solve the problem?
The method that seemed sufficient at a small scale often fails quietly as the amount of data grows. Users might try running the removal tool more often, thinking that doing it repeatedly will make up for the method's weak points; however, it doesn’t. Each run removes only exact matches, leaving variations untouched. As a result, the cleanup process becomes a recurring task on the calendar rather than a one-time solution, wasting time without resolving the underlying quality issue.
How do human limitations affect data handling?
Human brains are great at spotting identical repetition, but they have a hard time recognizing near-matching patterns when looking through thousands of rows. For instance, we can easily see that "Microsoft" and "microsoft" are the same name when they are next to each other. But when they are 400 rows apart with other data in between, they look like different entries when we check them manually. Tools like the Spreadsheet AI Tool help address this problem by analyzing patterns across entire columns simultaneously. This method differs from comparing each row individually.
What are the benefits of a pattern-based analysis approach?
This shift from looking for items one at a time to analyzing patterns catches differences that basic methods and simple duplicate removal might miss. It finds 'Microsoft Corporation', 'Microsoft Corp.', and 'MSFT' as likely mentions of the same company based on context and frequency, rather than just matching exact words. The practical difference shows in the quality of the output. A standard cleanup might lower 5,000 customer entries to 4,200 by removing exact duplicates. On the other hand, pattern-based analysis might reduce those entries to 3,800 by recognizing that 'ABC Company', 'ABC Co.', and 'ABC Company Inc.' all mean the same customer across different data sources. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool enhances this process by accurately identifying and consolidating data across various formats.
Why do users often feel their effort was sufficient?
That additional 400-row difference directly affects how accurately we report and how confident we are in our decisions. After spending an hour carefully removing duplicates, sorting columns, and checking results, it's easy to think the work is done. The time invested feels significant; the process is careful, and the clear outcome, with fewer rows, shows that something was done. This effort-based confidence makes it hard to accept that the method might be missing something important.
What is the core issue with the standard method?
Acknowledge that the method only catches exact matches. This means accepting that the hour was not wasted, but it also was not enough. This feeling of discomfort can be hard to deal with, so most people tend to just trust the process rather than question it. The real issue isn't the effort level. It's the mismatch between what the standard method actually does, which is to remove exact duplicate rows, and what users need it to do: consolidate all variations of the same entity. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool can help streamline this process by efficiently consolidating data for you.
What do users need to understand about duplicates?
This gap doesn't close just by careful clicking or waiting longer for verification. It needs either detailed manual normalization before removing duplicates or tools that can detect similarities, not just identical values. Many users never understand this important difference because it is often not explained. Tutorials usually show the ideal scenarios, while documentation only explains how to remove rows with exactly the same values. It doesn't make the practical limit clear: it doesn't see "John" and "john" as duplicates. Because of this, users often think our Spreadsheet AI Tool is smarter than it really is.
What is the challenge of practical alternatives?
Understanding the method's limitations is only useful if there is a practical alternative that doesn't require becoming a data engineer.
5 Practical Ways to Remove Duplicates in Google Sheets in Less Than 1 Minute

Google Sheets offers several ways to remove duplicates, each suited to different data conditions and cleanup goals. The quickest method takes only seconds if the data is already clean and the duplicates are identical. However, when dealing with real-world issues such as inconsistent capitalization, extra spaces, or different formats, you need methods that first standardize the data and then remove duplicates. The right method relies less on technical skills and more on understanding what a "duplicate" means in your specific dataset.
Start by selecting your data range, clicking on Data, and then choosing Remove Duplicates. After that, you can choose which columns define uniqueness, like Email, ID, or a mix of those, and then confirm your selection. The tool checks those columns and deletes rows where the values match exactly. For small, clean datasets where "John Smith" appears consistently, this process takes under 10 seconds. The speed of this method creates a sense of satisfaction. Rows disappear, counts decrease, and the sheet looks tighter. This method works great when importing from a single, well-kept system that uses consistent formatting.
For example, an export from a database that standardizes entries before output, or a carefully managed inventory list where product codes follow strict patterns, will clean up perfectly using this approach. If you're looking for a more efficient way to manage your data, consider how our Spreadsheet AI Tool can streamline this process and enhance your data management experience.
What are the limitations of immediate removal?
Limitations appear when data comes from different sources or involves human input. For example, customer names typed into web forms often have random capitalization. Email addresses copied from signatures may have extra spaces at the end, while company names taken from various systems might use "Inc." in one case and "Incorporated" in another. The tool treats "ABC Corp" and "ABC Corp " (with a trailing space) as distinct entries. As a result, both stay in the system because they're not exact matches, even though they clearly represent the same company.
Teams often use this tool and notice duplicates vanish, leading them to think the job is done. However, totals may still not match, and customer counts can still be too high. This issue arises from different expectations. The tool removes exact duplicate rows, but that doesn't mean it removes every variation of the same entity. For deeper insights, consider exploring how our Spreadsheet AI Tool can help you efficiently manage your data.
How can helper columns improve the process?
Creating a helper column next to your data improves accuracy. Use `=LOWER(TRIM(A2))` to change text to lowercase and get rid of extra spaces. Copy this formula down for all rows, then copy and paste the values to replace the formulas with their results. Now, use the Remove Duplicates tool on this cleaned column instead of the original. This two-step process works well to catch duplicates that might be missed by simply looking at them. For example, "Lagos" and "lagos" become the same after you use the LOWER function. Also, "John Doe" and "John Doe " (with a trailing space) match after TRIM removes the extra whitespace. This standardization converts unclear duplicates into exact matches, allowing the basic removal tool towork as it should.
Why is data preparation crucial?
According to Ben Collins, whose tutorial has received 37 user comments on troubleshooting tricky situations, this preparation step is what separates successful cleanups from those that didn't work. The tool itself never fails; instead, how you prepare the data decides if it finds real duplicates or just perfect duplicates.
The practical impact shows up in reporting accuracy. For example, a customer list with 3,000 entries might shrink to 2,700 using the basic tool (which removes only exact matches), but if you standardize it first, it might shrink to 2,400. This is because it catches the "Sarah Johnson" variations that just differ in spacing or case. That 300-entry difference directly affects segmentation counts, campaign targeting, and revenue attribution. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool enhances this process by streamlining data standardization, ensuring more accurate results.
This method requires a little more setup time, including creating the helper column, writing the formula, and converting the result to values. However, it closes the credibility gap caused by cleaning data that still yields inaccurate totals.
What is the COUNTIF technique?
To use the technique, add a helper column with `=COUNTIF(A:A, A2)`. This formula counts how many times each value appears in the entire column. Any cell with a value greater than 1 shows a duplicate. After that, filter the column to only show values above 1. Check the duplicates, then delete rows as needed.
This method changes control from automatic deletion to making informed choices. It lets users see every duplicate before they remove it. For example, if there are two customer entries, users can compare them to determine which one has better information, such as a full address instead of a partial one, a more recent contact date instead of an older one, or a verified email address instead of a placeholder. This way, it reduces the worry about deleting many entries without first checking them. If you're looking to streamline this process, our Spreadsheet AI Tool can automate data management.
Why do finance teams prefer this method?
Finance teams prefer this approach because accidental deletions in budget sheets or transaction logs create significant audit issues that can take days to resolve. By reviewing duplicates before removing them, the team can catch cases where what appears to be a duplicate is actually a legitimate, separate entry. For example, there could be two orders from the same customer on the same day, two employees with the same name, or two products with similar but different SKUs.
The tradeoff is speed for safety. While the basic tool finishes its job in seconds, this method needs manual review time that increases with the number of duplicates. For a sheet with 50 duplicates, the review takes a few minutes. For 500 duplicates, it gets boring. However, that careful review time stops a worse problem: accidentally deleting legitimate data and finding out about the loss only after someone asks why their order has disappeared from the system.
How do you define duplicates using multiple columns?
Select your full dataset and click Data, then Remove Duplicates. This time, select multiple columns that together define uniqueness. For example, a customer might appear twice if they placed orders on different dates (same Name + Email, different Date). Likewise, a product entry might repeat across regions (same Product + different Region). Defining duplicates correctly requires understanding which field combinations make a row truly redundant. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps with identifying duplicates efficiently.
Manual scanning fails in this situation because people can't retain multi-column patterns in working memory while scanning hundreds of rows. You might notice that "Sarah Johnson" appears three times, but miss that each instance is linked to a different order date. Also, you might delete all but one "Laptop" entry without realizing that each one represents inventory in a different warehouse.
What advantages does the tool have in terms of complexity?
The tool handles this complexity instantly. It allows users to say that Name and Email together uniquely identify a person. The tool keeps rows where that combination differs, while effectively removing actual duplicates. This stops both over-deletion, which can remove legitimate separate entries, and under-deletion, which keeps duplicates by checking only one column.
Ablebits explains seven easy ways to find duplicates, but most only focus on detecting them in a single column. This is where multi-column logic is important, as the accuracy of analytics depends on it. For example, revenue reports grouped by Product and Region need duplicates to be defined that way. Similarly, customer lifetime value calculations based on Email and Purchase Date rely on that combination to determine uniqueness. Getting the definition wrong harms all further analysis.
What issues arise with large datasets?
Large datasets pose a problem that no amount of manual formula work can efficiently fix. The same company may appear as Microsoft, Microsoft Corporation, MSFT, and Microsoft Corp. across different data sources. These are semantically identical entries, but are structured differently. Traditional methods force you to choose: spend hours creating lookup tables to map these differences, or accept a higher unique company count. Neither option works well when combining vendor lists, customer databases, or survey responses that have collected variations over time. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool streamlines this process by intelligently recognizing and unifying these variations.
How does the AI tool handle duplicates?
'Spreadsheet AI Tool' addresses this by analyzing context patterns rather than simply checking whether letters are the same. Rather than asking, "are these characters identical?" It asks, "Do these entries likely represent the same entity based on usage patterns and semantic similarity?" This helps catch different ways of saying the same thing that exact matching and basic cleanup miss, bringing together entries that clearly refer to the same thing but could go unnoticed by regular methods.
The practical difference shows up in datasets where entities have multiple acceptable names. For example, in product catalogs, "T-shirt" and "Tee" mean the same item. In contact lists, "Robert" and "Bob" represent the same person. In geographic data, "NYC", "New York City", and "New York, NY" all point to the same location. Pattern-based analysis finds these connections without needing you to list every possible variation manually.
What is the benefit of automated pattern-based detection?
This becomes especially valuable in recurring cleanup scenarios. Monthly imports from CRM systems, quarterly vendor reconciliations, and weekly survey consolidations all introduce duplicates with slight differences. Setting up pattern-based detection once removes the need to manually find new variations each time. The speed advantage isn't just about time saved; it's also about relieving the mental burden of always wondering whether all duplicates were caught or if totals are still high because of unexpected variations. When the cleanup process considers semantic similarity rather than just exact matching, the results become reliable enough to make decisions. However, speed and accuracy only matter if you know which method to use for your specific situation.
What You Should Do Now (See Results in Under 1 Minute)
Start with one column. Pick something specific, like Email, Name, ID, or Phone number. Keeping a smaller scope helps you quickly determine whether your data is truly clean or just appears clean. This method isn't about being overly careful; it's about getting feedback right away. If you spend 20 minutes cleaning the entire sheet, you might find you chose the wrong range or didn't understand which columns indicate uniqueness.
Look at your sheet to find the field that probably has duplicates. This could include customer emails from different campaigns, product SKUs combined from various warehouses, or employee IDs from payroll and HR systems. No matter which column represents the entity you're trying to count or analyze, that should be your starting point. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps automate this process, giving you insights faster and making data management more efficient.
This focus is important because you need quick confirmation that the method works before using it on the whole dataset. If you select all columns at once and it fails, you won’t know which field caused the problem or if your idea of duplicate matches what the tool actually deleted. Starting small gives you a controlled test that either boosts your confidence or reveals problems while the stakes are still low.
How do you set up conditional formatting?
Select the column. Click Format, then Conditional formatting. Under "Format cells if," choose "Custom formula is." Enter `=COUNTIF(A:A, A1)>1`, changing the column letter to match yours. Pick a highlight color, then click Done. What happens next is the moment most people realize their sheet isn't as clean as they thought. Rows that you thought were unique light up across the entire dataset. Duplicates, separated by hundreds of entries, suddenly become visible. Variations you might have missed while scanning manually, because who actually reads every row when there are 3,000? now announce themselves in bright yellow or red, allowing for efficient application of conditional formatting. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps automate this process, making it easier to manage your data.
What should you do after identifying duplicates?
Now that duplicates are visible, scan only the highlighted rows. Confirm which entries are truly duplicates and which ones look similar but represent different entities. When you find legitimate duplicates, identify which record should remain. Should it be the most recent, the most complete, or the first entered?This decision step prevents the anxiety that comes from blind deletion.
You are not relying on a tool to make judgment calls about your data; instead, you use the tool to find patterns, just like how our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps identify data discrepancies. Then, by applying human context, you can decide what "duplicate" actually means in this specific situation. Sometimes "John Smith" appearing twice is an error, while other times it may be two different people who happen to share a common name. The highlight does not make that call; you do.
How can you remove duplicates effectively?
Once you're sure about what should be removed, choose your data range. Click Data, then select Remove duplicates. Pick the right column or columns that show uniqueness and confirm your choice. The rows disappear, not just the clear duplicates next to each other, but also those mixed throughout the sheet. These hidden duplicates might have escaped notice during manual cleanup because they were too far apart. This process finishes in seconds, whether you have 200 rows or 20,000. Speed isn't the only advantage; it also gets rid of the worry about whether you found everything. For even greater efficiency, consider how our Spreadsheet AI Tool can automate data-handling tasks.
What if duplicates vary in format?
For datasets where the same entity appears with variations, such as different capitalization, extra spaces, or slight name differences, pattern-based tools like the Spreadsheet AI Tool extend this logic by recognizing semantic similarity rather than just exact matches. This means that "Microsoft Corp" and "Microsoft Corporation" get flagged as likely duplicates, even though traditional methods would treat them as separate entries. The result is a cleaner consolidation without the need for manual lookup tables or hours spent standardizing formats before removal.
How do you verify the effectiveness of your cleanup?
Run a quick check. Do the totals make sense? Do the counts match what you expected? Have the highlights disappeared? This confirmation shows whether the cleanup worked or if you need to make changes. If the numbers still seem wrong, the problem might be because of duplicates that exist in multiple columns, not just the one you checked. Also, differences in formatting could stop exact matches. Luckily, you can find these problems in seconds with our Spreadsheet AI Tool, instead of waiting until you’ve built an entire report on unclear data classification.
Why is speed important in the cleanup process?
The speed of validation is just as important as the speed of removal. When the process lets you test, adjust, and confirm in less than a minute, iteration becomes practical. You aren't stuck with just one method that either works perfectly or fails completely; you can improve your approach in real time using the actual data. What you've achieved is more than just saving time. You've successfully removed duplicates without having to scan manually or guess which rows to delete, and you've avoided the risk of missing variations that could be hiding in plain sight. Most importantly, you can now trust your data again. The counts are accurate, the totals match, and the worry about whether your analysis is based on inflated numbers has just gone away.
How can you streamline the process for future tasks?
For tasks that happen often, real efficiency comes from not having to set things up again and again. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool simplifies this process by automating repetitive tasks, allowing you to focus on more important aspects of your work.
Related Reading
Clean Your Sheet in Under 1 Minute
If formulas or setup slow you down, explaining what a duplicate is in simple words can help you understand your logic better. This way, you don’t have to guess and check, which might miss differences. With clear rules, you can clean up accurately the first time, saving you time and preventing mistakes that could mess up your work later. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool simplifies data management, allowing you to streamline your cleaning process effortlessly.
The gap between effort and accuracy
The typical cleanup workflow requires knowing which formula works for each variation. For example, does TRIM remove trailing spaces? Does LOWER handle mixed case? Which combination sets apart "New York" from "new york" and "New York"? Each question requires either existing technical knowledge or time spent reviewing documentation and testing formulas on sample data. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool simplifies this process by automating common tasks efficiently. This creates a problem that many solve by doing the same task over and over. You run the cleanup, check the totals, and realize something still seems off. Then, you add another formula and run it again.
Each round takes minutes, and after three or four tries, you've spent twenty minutes on what should have been a one-minute task. The real cost goes beyond time, as it includes the mental overhead of keeping multiple formula variations in your mind while trying to remember which columns have been done and which still need work.
When Describing the Problem Becomes Faster Than Solving It Technically
What if you could explain the cleanup rule the same way you'd tell a colleague? Remove rows where the company name is the same, ignoring capitalization and extra spaces. This sentence contains the complete logic, and a human understands it instantly. In contrast, traditional spreadsheet tools require translating that logic into nested functions, helper columns, and multi-step processes.
Spreadsheet AI Tool allows you to describe deduplication rules in plain English and handles the translation into working logic. Instead of constructing `=LOWER(TRIM(A2))`, copying it down a helper column, and then running remove duplicates on that column before deleting the helper column, you simply state what makes entries equivalent. The system then validates whether rows match that definition. This approach shifts the bottleneck from technical implementation to clear thinking about what duplication actually means in your context.
The speed advantage compounds when your definition of duplicate involves multiple conditions. For instance, the same email address and the same company name, but different order dates, should stay separate, which can become complex to implement with formulas. You would need COUNTIFS with multiple criteria, careful range references, and correctly chained logical operators. Describing the rule in natural language bypasses that translation step entirely.
The Confidence That Comes from First-Pass Accuracy
Getting cleanup right the first time eliminates a certain kind of anxiety. When you run a process and trust the result immediately, you can move forward with confidence. On the other hand, if you run a process and wonder whether it caught everything, hesitation starts to creep in. This hesitation can affect the work that comes after. Questions pop up: Should you send this report to the executive team? Should you base budget decisions on these customer counts? Should you trust the segmentation analysis built on this data?
Pattern-based validation helps eliminate that hesitation. When the system confirms that "Microsoft Corporation" and "Microsoft Corp." are the same based on meaning, not just character matches, you feel assured that variations were caught without having to guess every possible formatting difference. The cleanup process becomes more complete instead of just partial. This change affects how you work with the output; you can use it right away, without having to double-check it manually. With Numerous, our innovative Spreadsheet AI Tool ensures you can trust your data from the first pass.
Setup time versus recurring time
Building the perfect formula setup can take 30 minutes. If you only clean this dataset once, that investment makes sense. However, most duplicate issues recur, including monthly CRM exports, weekly survey consolidations, and quarterly vendor reconciliations. Each cycle brings changes because data sources do not align on their formatting standards.
Teams respond by saving their formula setup in a template sheet and copying it each time new data arrives. This method works until the data structure changes a bit; maybe a new column shows up, the header row moves, or someone renames a field. When that happens, the saved formulas stop working, and you end up fixing cell references rather than cleaning the data.
Describing cleanup rules in simple language makes them useful across data changes. The instruction to "consolidate entries where email matches, ignoring case and whitespace" works regardless of whether the email column is called Email, Email Address, or Contact Email. The logic stays stable even when the technical structure changes. Our Spreadsheet AI Tool helps streamline these data processes, making your cleanup more efficient.